Regenerative medicine is an innovative field that holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare by harnessing the body’s own healing capabilities. This cutting-edge approach aims to repair, replace, and regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering hope for individuals with chronic diseases and injuries. In this article, we will delve into the world of the power of regenerative medicine, exploring its principles, breakthroughs, and potential applications, while shedding light on its transformative impact on modern healthcare.

Understanding The Power Of The Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine encompasses a range of techniques and therapies that aim to restore, replace, or regenerate damaged cells, tissues, or organs. It leverages the body’s natural ability to heal itself, employing innovative approaches to promote tissue regeneration and functional restoration. By utilizing stem cells, tissue engineering, gene therapy, and other advanced methodologies, regenerative medicine pioneers a new frontier in healthcare.
The Three Pillars of Regenerative Medicine
The power of the regenerative medicine is built upon three fundamental pillars:
Tissue Engineering: This involves creating functional tissues and organs in the laboratory by combining cells, scaffolds, and bioactive factors. Researchers aim to develop tissues that can be transplanted into patients, offering long-lasting solutions for organ failure and tissue damage.
Cellular Therapy: This approach involves using stem cells, which have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, to repair damaged tissues. Stem cells can be obtained from different sources, such as embryos, adult tissues, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
Medical Devices and Artificial Organs: These innovative technologies provide mechanical support or replace the function of diseased organs. From artificial hearts to prosthetic limbs, medical devices play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for patients.
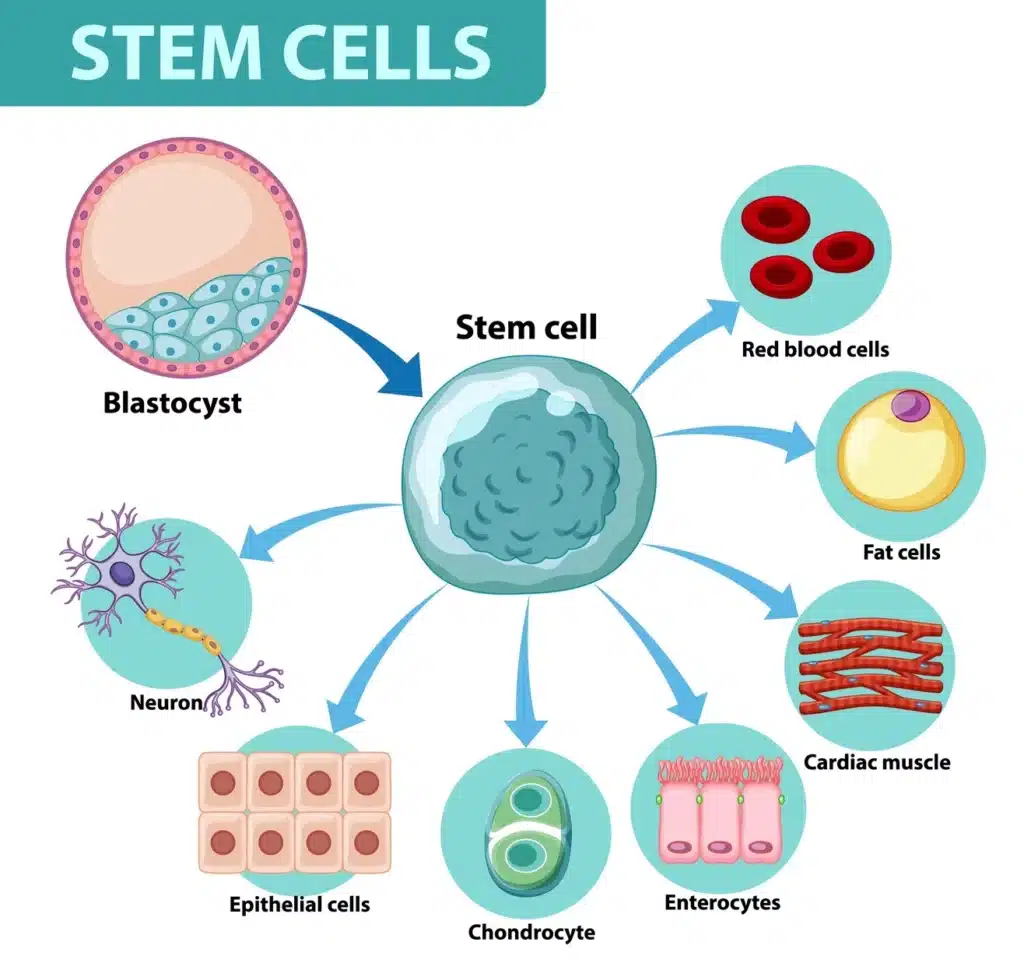
Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
Embryonic Stem Cells: Embryonic stem cells, derived from early-stage embryos, possess remarkable regenerative potential. They can develop into any cell type in the body, making them a valuable resource for repairing damaged tissues. However, ethical considerations surround their use, limiting their application.
Adult Stem Cells: Adult stem cells are found in various tissues and organs throughout the body. These cells play a crucial role in tissue maintenance and repair. They can differentiate into specific cell types, making them ideal for regenerative therapies. Examples include hematopoietic stem cells found in bone marrow and mesenchymal stem cells found in adipose tissue.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to exhibit pluripotent characteristics similar to embryonic stem cells. This breakthrough discovery has eliminated the need for embryonic stem cells, as iPSCs offer a potentially unlimited supply of patient-specific cells for regenerative therapies.
Applications of Regenerative Medicine
It holds tremendous potential across a wide range of medical conditions and injuries. Let’s explore some of its most promising applications and the power of the regenerative medicine:
A. Organ Regeneration
One of the most exciting prospects of regenerative medicine is the ability to regenerate whole organs. Scientists are making significant strides in engineering functional organs, such as hearts, kidneys, and livers, using a patient’s own cells. This could alleviate the organ shortage crisis and eliminate the need for transplant waiting lists.
B. Tissue Repair and Wound Healing
Regenerative medicine offers hope for individuals with chronic wounds or injuries. By stimulating the body’s regenerative processes, scientists are developing therapies to accelerate wound healing and promote tissue regeneration, which could significantly improve the quality of life for patients suffering from conditions like diabetic ulcers and severe burns.
C. Neurodegenerative Diseases
The power of the regenerative medicine holds promise for treating neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to replace damaged neurons and restore brain function. Although these therapies are still in the early stages of development, they offer a glimmer of hope for patients with currently incurable conditions.

D. Musculoskeletal Disorders
Conditions like osteoarthritis and cartilage injuries can cause significant pain and disability. The power of the regenerative medicine offers potential treatments that aim to restore damaged cartilage and joints, alleviating pain and improving mobility. Techniques like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and mesenchymal stem cell therapy show promise in this area.

Challenges and Future Outlook for the Regenerative Medicine
While it holds immense promise, it also faces several challenges on its path to widespread adoption.
A. Ethical Considerations
The use of embryonic stem cells raises ethical concerns for some individuals. However, advancements in cellular reprogramming techniques, such as iPSCs, offer an alternative approach that bypasses these ethical dilemmas. Striking a balance between scientific progress and ethical considerations remains an ongoing discussion in the field.
B. Regulatory Hurdles
Bringing regenerative medicine therapies from the laboratory to the clinic involves navigating complex regulatory pathways. Ensuring safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes is crucial for the success of these innovative treatments. Regulatory agencies worldwide are working to establish guidelines to streamline the approval process while safeguarding patient welfare.
C. Cost and Accessibility
The high cost associated with regenerative medicine treatments is a significant hurdle to their widespread implementation. As technology advances and economies of scale come into play, it is anticipated that costs will decrease over time. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve accessibility to these therapies, ensuring they reach a broader population.

Conclusion
The power of the regenerative medicine represents a transformative approach to healthcare, offering hope for patients with currently incurable conditions and injuries. Through tissue engineering, cellular therapy, and the development of medical devices, scientists are revolutionizing the way we treat diseases and heal the human body. While challenges exist, the potential for regenerative medicine to improve lives is undeniable. As research and innovation continue, we eagerly anticipate a future where the power of the regenerative medicine plays a central role in restoring health and enhancing well-being.