Introduction
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a promising therapeutic approach in the field of regenerative medicine. It is a concentrated form of plasma that contains a high concentration of platelets and growth factors, which play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of PRP, exploring its composition, preparation techniques, medical applications, efficacy, and future prospects.
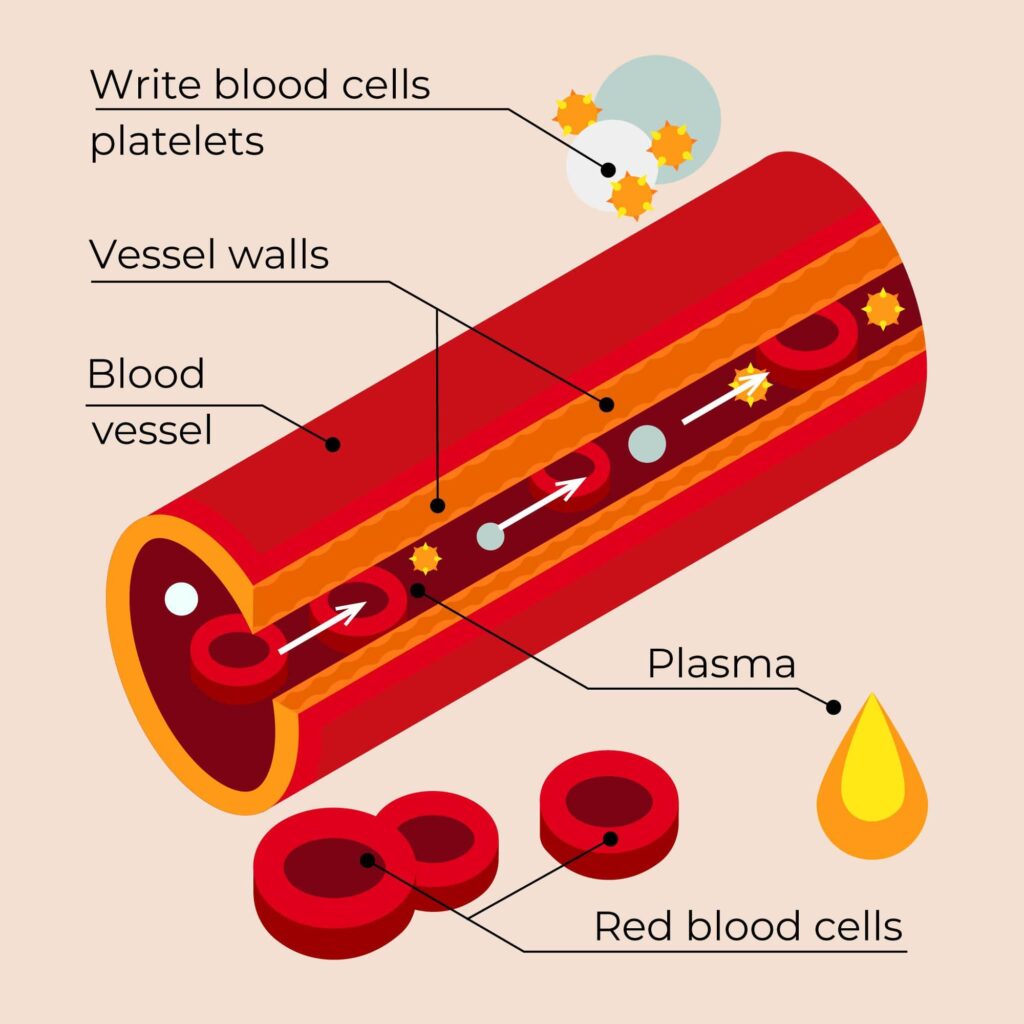
Composition of Platelet Rich Plasma
Platelets, the key component of PRP, are tiny cellular fragments that circulate in the blood. While their primary function is to initiate clotting and prevent bleeding, platelets also harbor a rich reservoir of growth factors. These growth factors are responsible for stimulating cellular activities that promote tissue healing and regeneration. Plasma, on the other hand, is the liquid component of blood that carries cells, nutrients, hormones, and other substances throughout the body.
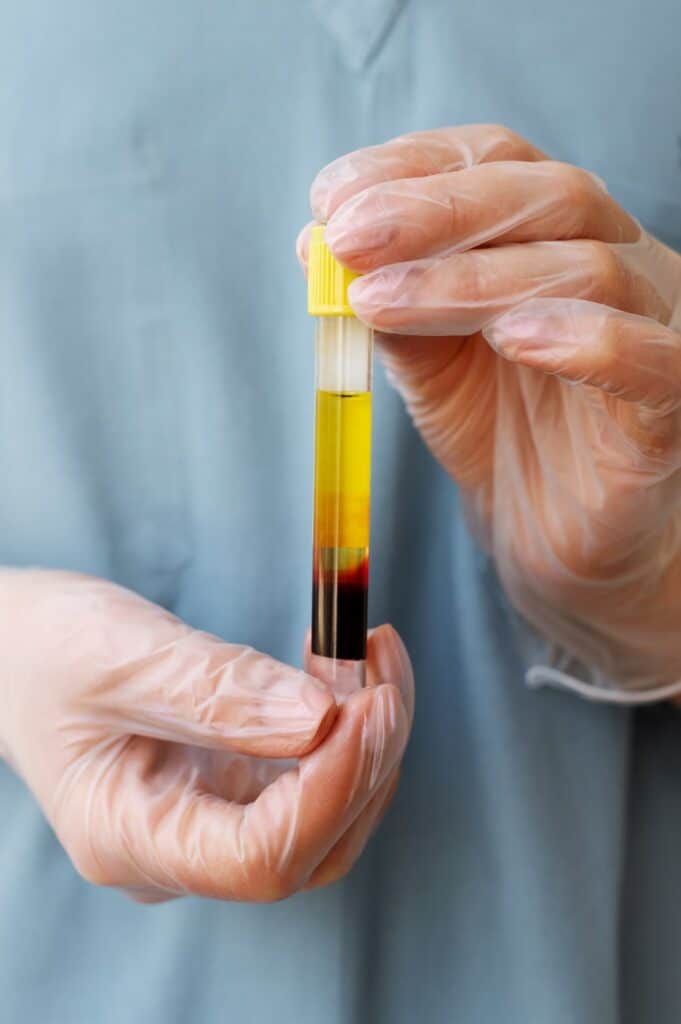
Preparation of Platelet Rich Plasma
To obtain PRP, a small blood sample is collected from the patient. The blood is then subjected to a centrifugation process, which separates the platelets from other blood components based on their density. Various types of centrifuges, such as fixed-angle and swing-bucket, are utilized for this purpose. The centrifugation process allows the separation of platelet-rich plasma from platelet-poor plasma and red blood cells, resulting in a concentrated PRP product.
Growth Factors in Platelet Rich Plasma
PRP is rich in growth factors that regulate cellular activities and promote tissue regeneration. These growth factors include Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), and Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF). Each of these growth factors plays a unique role in stimulating cellular proliferation, angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and extracellular matrix synthesis.
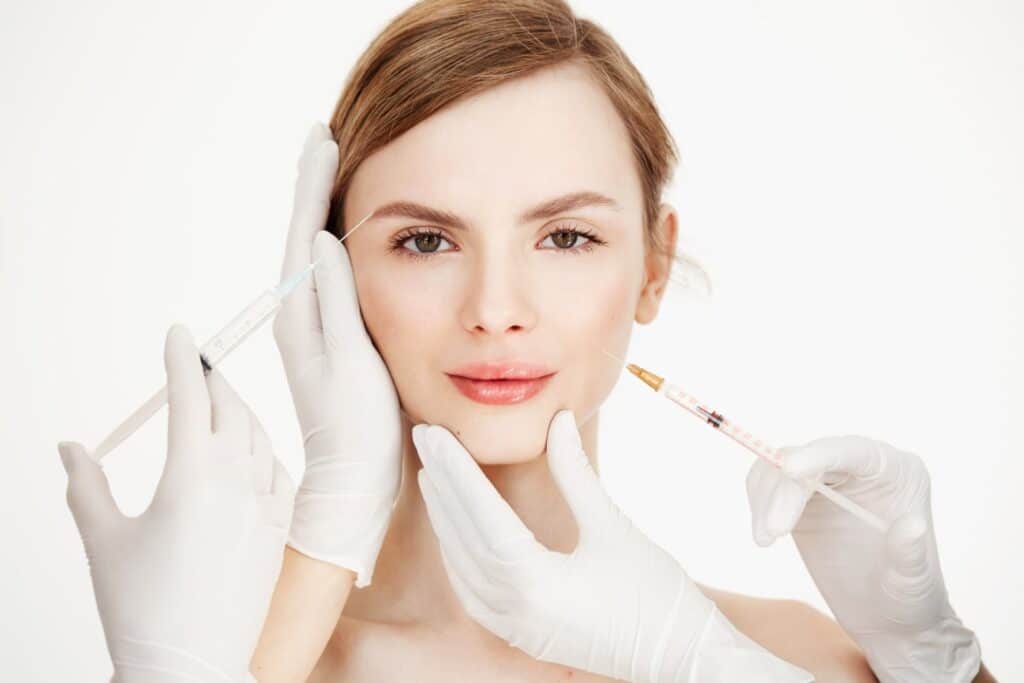

Medical Applications of Platelet Rich Plasma
The versatility of PRP has led to its application in various medical fields. In orthopedics, PRP is used for the treatment of joint injuries such as tennis elbow, Achilles tendonitis, and osteoarthritis. The growth factors in PRP help reduce pain and inflammation while promoting tissue repair. Additionally, PRP has shown promising results in accelerating bone healing, making it a valuable adjunct in fracture management.
Dermatology has also embraced the therapeutic potential of PRP. In aesthetic medicine, PRP is used for skin rejuvenation, where it stimulates collagen production and enhances skin texture and tone. Furthermore, PRP has gained recognition in hair restoration treatments, effectively promoting hair growth and improving hair thickness and quality.
The dental field has not been left untouched by the benefits of PRP. Dentists utilize PRP in dental implant procedures to accelerate osseointegration, the process by which the implant fuses with the surrounding bone. PRP has also shown promise in the treatment of gum diseases, aiding in tissue regeneration and promoting periodontal health.
Efficacy and Safety of Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of PRP therapy in various applications. However, it is important to note that individual responses may vary, and more research is needed to establish standardized protocols and guidelines for optimal outcomes. As with any medical procedure, PRP therapy carries potential risks and side effects. These include infection, allergic reactions, pain, discomfort, and hematoma formation. It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to assess the suitability and safety of PRP therapy for each individual case.
PRP vs. Alternative Treatments
When comparing PRP with alternative treatments, such as corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections, several factors come into play. While corticosteroids provide short-term relief by reducing inflammation, their long-term effects on tissue regeneration are limited. Hyaluronic acid injections, commonly used for joint lubrication in osteoarthritis, offer symptomatic relief but lack the regenerative properties of PRP. PRP, with its concentration of growth factors, offers a unique approach by promoting both symptom relief and tissue repair.
PRP Preparation Techniques
Different PRP preparation techniques are employed, depending on the desired platelet concentration and therapeutic application. The single spin technique involves a single centrifugation step to separate PRP from the whole blood. The double spin technique further refines the separation process by performing an additional centrifugation step to concentrate the platelets. The buffy coat technique involves the removal of the buffy coat layer, which contains a higher platelet concentration, from the blood sample. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the intended use of PRP and the desired platelet concentration.
Factors Affecting Platelet Rich Plasma Quality
Several factors influence the quality of PRP obtained. Donor variability, such as age, overall health, and underlying medical conditions, can affect the composition and efficacy of PRP. The choice of anticoagulants used during sample collection can also impact the final PRP product. Additionally, the centrifugation speed and duration, as well as the storage conditions of PRP, can influence the platelet concentration and growth factor activity. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial to ensure the consistency and effectiveness of PRP therapy.
Future Perspectives and Innovations in Platelet Rich Plasma therapy
Ongoing research continues to explore the vast potential of PRP therapy. Emerging advancements include the combination of PRP with other regenerative therapies, such as stem cells, to enhance tissue healing and regeneration. Furthermore, innovations in PRP preparation techniques aim to improve standardization and customization, catering to specific medical conditions and patient needs. The future holds promising prospects for PRP as a regenerative therapy, with continued refinement and expanded applications.
Conclusion
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) has revolutionized the field of regenerative medicine with its ability to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Through the concentration of platelets and growth factors, PRP offers a versatile therapeutic approach in various medical specialties. From orthopedics to dermatology and dentistry, PRP has demonstrated its potential to promote tissue repair and regeneration. While further research is needed to optimize protocols and establish guidelines, the future of PRP therapy looks bright. With ongoing innovations and advancements, PRP continues to pave the way for regenerative medicine, unlocking new possibilities for patients seeking effective and natural solutions for their health concerns.